Hampton Research蛋白结晶试剂盒






Products > Optimize Reagents > Optimize – Monoolein > Monoolein
Monoolein
Applications
- LCP – Lipidic Cubic Phase
Features
- Purity >99%
- Host lipid for LCP Lipidic Cubic Phase
- Monoolein forms a LCP Lipidic Cubic Phase when mixes with protein solution
Description
Synonyms: 1-(cis-9-Octadecenoyl)-rac-glycerol, rac-Glycerol 1-monooleate, DL-α-Monoolein, Glyceryl cis-9-octadecenoate, 1-Oleoyl-rac-glycerol, 9-monoolein, 9-monooctadecanoin, 9.9 MAG
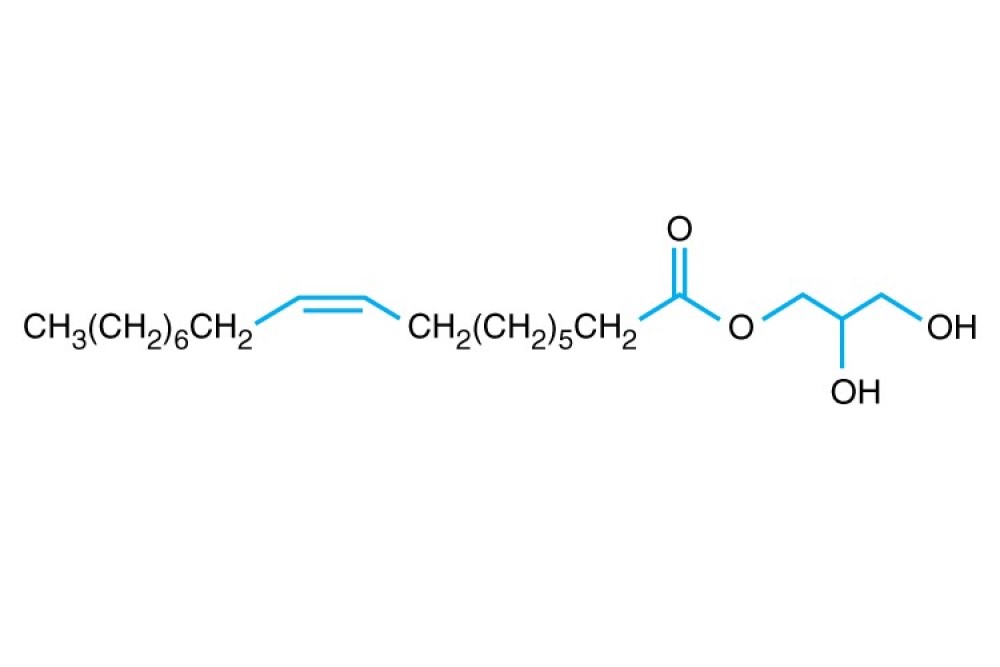
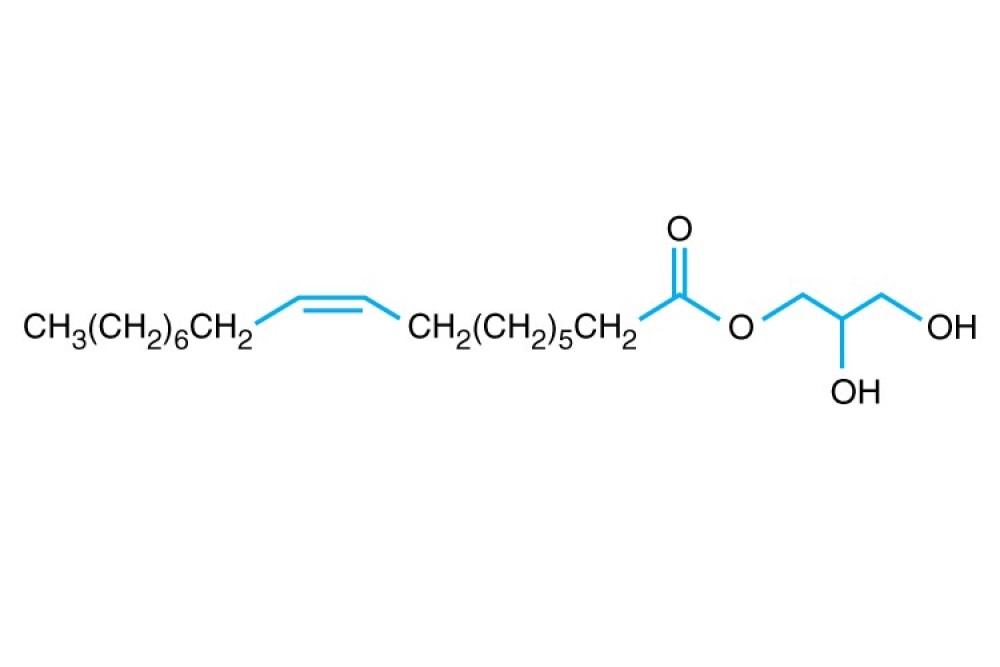
Formula C21H40O4
Linear Formula CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOCH2CHOHCH2OH
Formula Weight (Mr) 356.50
CAS Number [111-03-5]
EC Number 203-827-7
Beilstein Registry Number 1728976
MDL Number MFCD00042735
PubChem Substance ID 24897178
Appearance (starting material) Clear colorless liquid to white waxy solid at room temperature
Purity >99% by Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
Gas liquid chromatography > 99% on methyl ester
Thin layer chromatography shows only the monoglyceride moiety present
Type Non-ionic
Melting Point 35°C
Original source Sunflower oil
Infrared spectrum Conforms to structure
Storage
Store at 0 degrees Celsius or colder.
Unopened product best if used within 24 months of receipt. Once opened, best if used within 6 months. To enhance the stability of remaining material after product is opened, gently purge the product with an inert gas such as nitrogen or argon, which will remove oxygen which can cause oxidation of the Monoolein, before sealing.
Solubility
Soluble in chloroform (50 mg/ml). Soluble in Hexane and can be crystallized from Hexane. In water, Monoolein tends to form a gel or emulsion.

Click to Zoom In
CAT NO
HR2-435
NAME
DESCRIPTION
1 gram
PRICE
$100.00
cart quote
Support Material(s)
 HR2-435 Monoolein SDS
HR2-435 Monoolein SDS HR2-436 Monoolein SDS
HR2-436 Monoolein SDS Certificate Of Analysis
References
1. Data for Biochemical Research, 3rd ed., Dawson, R. M. C., et al., Oxford University Press (New York, NY: 1986), pp. 178-179.
2. Membrane protein crystallization in lipidic mesophases: detergent effects. Ai X, Caffrey M. Biophys J. 2000 Jul;79(1):394-405.
3. Membrane protein crystallization in meso: lipid type-tailoring of the cubic phase. Cherezov V, Clogston J, Misquitta Y, Abdel-Gawad W, Caffrey M. Biophys J. 2002 Dec;83(6):3393-407.
4. Crystallization screens: compatibility with the lipidic cubic phase for in meso crystallization of membrane proteins. Cherezov V, Fersi H, Caffrey M. Biophys J. 2001 Jul;81(1):225-42.
5. A fast, simple and robust protocol for growing crystals in the lipidic cubic phase. Aherne M, Lyons JA, Caffrey M. J Appl Crystallogr. 2012 Dec 1;45(Pt 6):1330-1333. Epub 2012 Oct 10.
6. Membrane protein structure determination using crystallography and lipidic mesophases: recent advances and successes. Caffrey M, Li D, Dukkipati A. Biochemistry. 2012 Aug 14;51(32):6266-88. doi: 10.1021/bi300010w. Epub 2012 Jul 31.
7. Crystallizing membrane proteins for structure-function studies using lipidic mesophases. Caffrey M. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Jun;39(3):725-32. doi: 10.1042/BST0390725.
8. Monoolein: a magic lipid? Kulkarni CV, Wachter W, Iglesias-Salto G, Engelskirchen S, Ahualli S. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2011 Feb 28;13(8):3004-21. doi: 10.1039/c0cp01539c. Epub 2010 Dec 23.
9. Crystallizing membrane proteins using lipidic mesophases. . Caffrey, M., and V. Cherezov. (2009). Nat. Protoc. 4: 706-731.
10. Detergents destabilize the cubic phase of monoolein: implications for membrane protein crystallization. Misquitta, Y, and M. Caffrey. (2003). Biophys. J. 85: 3084-3096.
11. Reconstitution of protein in Lipidic Cubic Phase (Monoolein)http://cherezov.scripps.edu/reconstitution.htm.
12. Lipid Mixing http://cherezov.scripps.edu/lipmix.htm.
13. Lipidic Cubic Phase Resources http://cherezov.scripps.edu/resources.htm.
14. Crystallization of Membrane Proteins in Lipidic Cubic Phases http://www.jove.com/video/2501/crystallization-of-membrane-proteins-in-lipidic-mesophases.
15. Crystallizing Membrane Proteins for Structure Determination using Lipidic Mesophases http://www.jove.com/video/1712/crystallizing-membrane-proteins-for-structure-determination-using.


Hampton Research, first in crystallization since 1991, developing and delivering crystallization and optimization screens, reagents, plates, and other tools for the crystallization of biological macromolecules, including proteins (antibody), peptides (insulin), and nucleic acids (DNA).
- Products
- Gallery
- My Account
|
|
|
- Contact Us
- Quick Order
- Support
|
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
|
- Products
- Gallery
- My Account
- Support
- Contact Us
- Quick Order
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
© 2021 HAMPTON RESEARCH CORP.
| Website by Skyhound Internet